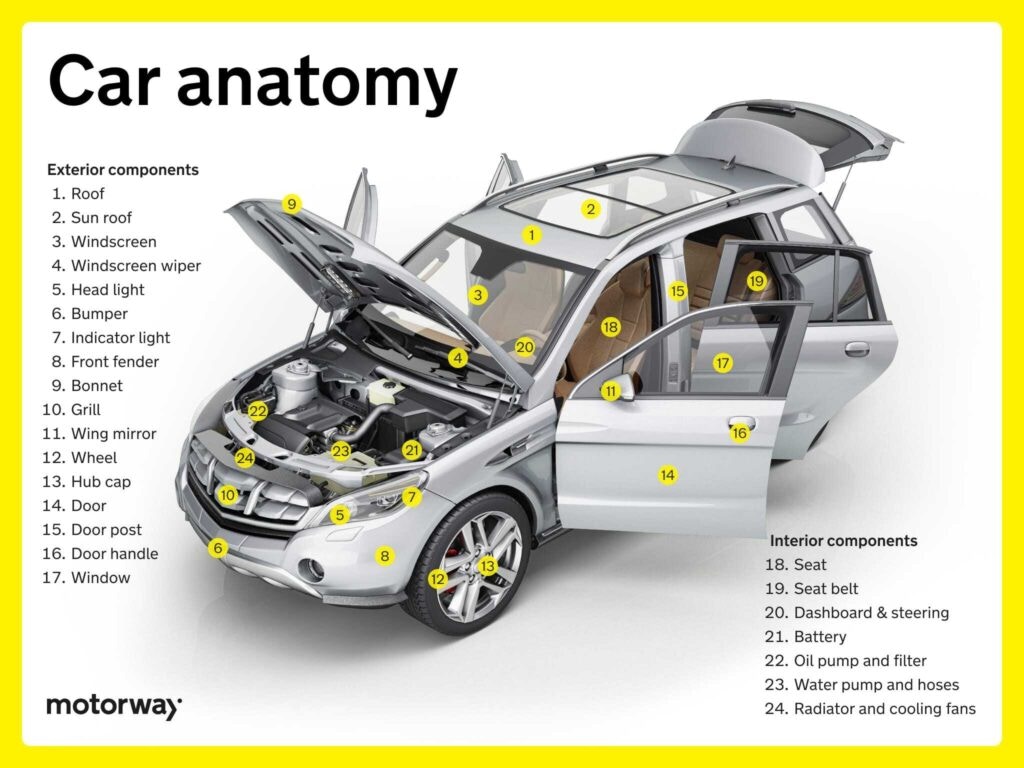
When most people think of cars, they usually picture the engine, tires, or sleek exterior. Yet, beneath the surface lies a complex framework that ensures every vehicle remains safe, functional, and durable. Automotive structural parts form the backbone of your car, shaping its performance, protecting passengers, and contributing to overall efficiency. Understanding these essential components can deepen your appreciation for modern vehicles and help you make smarter maintenance decisions.
The Chassis: The Heart of Your Car’s Structure
The chassis serves as the main framework of a car. Think of it as the skeleton that holds everything together. Made from steel, aluminum, or advanced composites, the chassis supports the weight of the engine, transmission, suspension, and body. Its primary role is to provide rigidity while absorbing and distributing forces during driving, cornering, and, most importantly, in collisions.
Modern chassis designs are a marvel of engineering. They balance strength with weight reduction to improve fuel efficiency without compromising safety. Manufacturers often reinforce critical areas using high-strength steel or aluminum alloys, creating crumple zones that absorb energy in an accident, protecting occupants.
The Frame: Strength Beneath the Body
In many vehicles, especially trucks and SUVs, the frame serves as the foundational structure. Unlike the chassis in unibody vehicles (where the body and frame are integrated), a separate frame provides added durability for heavy-duty tasks. Frames can be ladder-type, perimeter, or space-frame designs, each optimized for specific driving needs.
A ladder frame, for example, is popular in trucks due to its ability to handle heavy loads and off-road conditions. On the other hand, space-frame structures, often found in sports cars, prioritize lightweight rigidity, improving speed and handling. Regardless of type, the frame acts as the backbone, ensuring all other components remain aligned and stable.
Suspension Mounts and Subframes: Linking Wheels to the Car
The suspension system connects the vehicle to its wheels and absorbs shocks from the road. Integral to this system are suspension mounts and subframes, which secure the suspension components while isolating vibrations from the cabin.
Subframes are smaller structural units attached to the main chassis, often carrying the engine, transmission, or suspension assembly. They play a crucial role in maintaining precise alignment, which enhances handling and tire longevity. Well-designed subframes and mounts improve ride comfort, reduce noise, and contribute to the overall structural integrity of the vehicle.
Crumple Zones and Reinforcements: Safety First
Modern automotive design heavily emphasizes safety, and this is where crumple zones and reinforcements come into play. Crumple zones are strategically engineered sections of the car, usually at the front and rear, designed to deform during a collision. By absorbing kinetic energy, they reduce the force transmitted to passengers.
Reinforcements, such as side-impact bars and reinforced roof structures, further protect occupants during accidents. These components are often invisible to the naked eye but are critical for meeting safety regulations and ensuring a vehicle performs well in crash tests.
Body Panels and Structural Integration
While body panels are often thought of as purely aesthetic, they also contribute to structural integrity. Components like the roof, floor pan, and pillars (A, B, and C pillars) provide rigidity and help distribute forces throughout the vehicle. In unibody designs, the integration of panels and frame means that the body itself contributes to overall strength.
This structural integration allows manufacturers to reduce weight without sacrificing safety. The result is a more fuel-efficient vehicle that still meets stringent safety standards.
Importance of Maintenance and Inspection
Though structural parts are designed to last the life of a vehicle, they are not entirely immune to wear and damage. Corrosion, rust, or previous accidents can compromise structural integrity. Regular inspections, particularly after collisions, are crucial to ensure safety. Certified mechanics can detect subtle issues in frames, subframes, or mounts that might not be obvious but could affect performance or protection.
If you ever need to move your vehicle safely from one location to another, you can rely on Devon car transporters for professional and secure transportation services. To know everything in detail, check here – https://www.shiply.com/car-transporters/devon-car-transporters.
In Conclusion
Automotive structural parts go far beyond simple metal and bolts—they form the hidden framework that ensures your car’s performance, safety, and durability. From the chassis and frame to subframes, crumple zones, and reinforced panels, each element plays a vital role in your vehicle’s operation and protection. Increasingly, heavy injection molding is being used to create robust, lightweight components that enhance structural integrity while reducing overall vehicle weight.
Understanding these parts gives car owners a deeper appreciation for the advanced engineering in modern vehicles and underscores the importance of proper maintenance. The next time you drive, remember that your car’s true strength lies beneath the surface, in the carefully engineered structure that keeps you safe on every journey.